We will emphasize the interconnectedness of vascular networks as a “general” perspective on anatomy, variation, and adaptation. “Balance” and “spectrum” are key words — not “normal” and “variation”. To this end, the following diagrams will serve as keys and guides. In figures below, numbers point to same vessels.

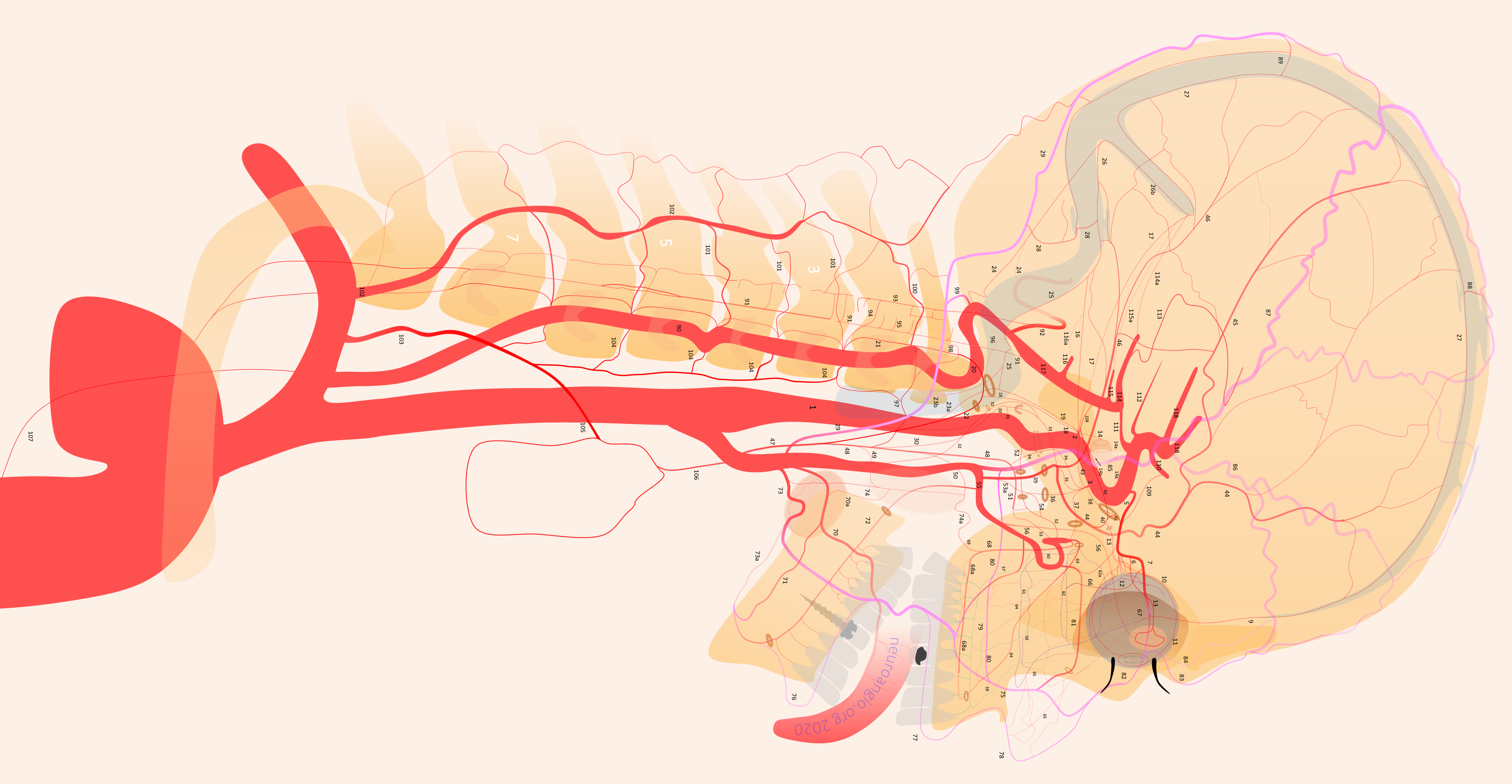
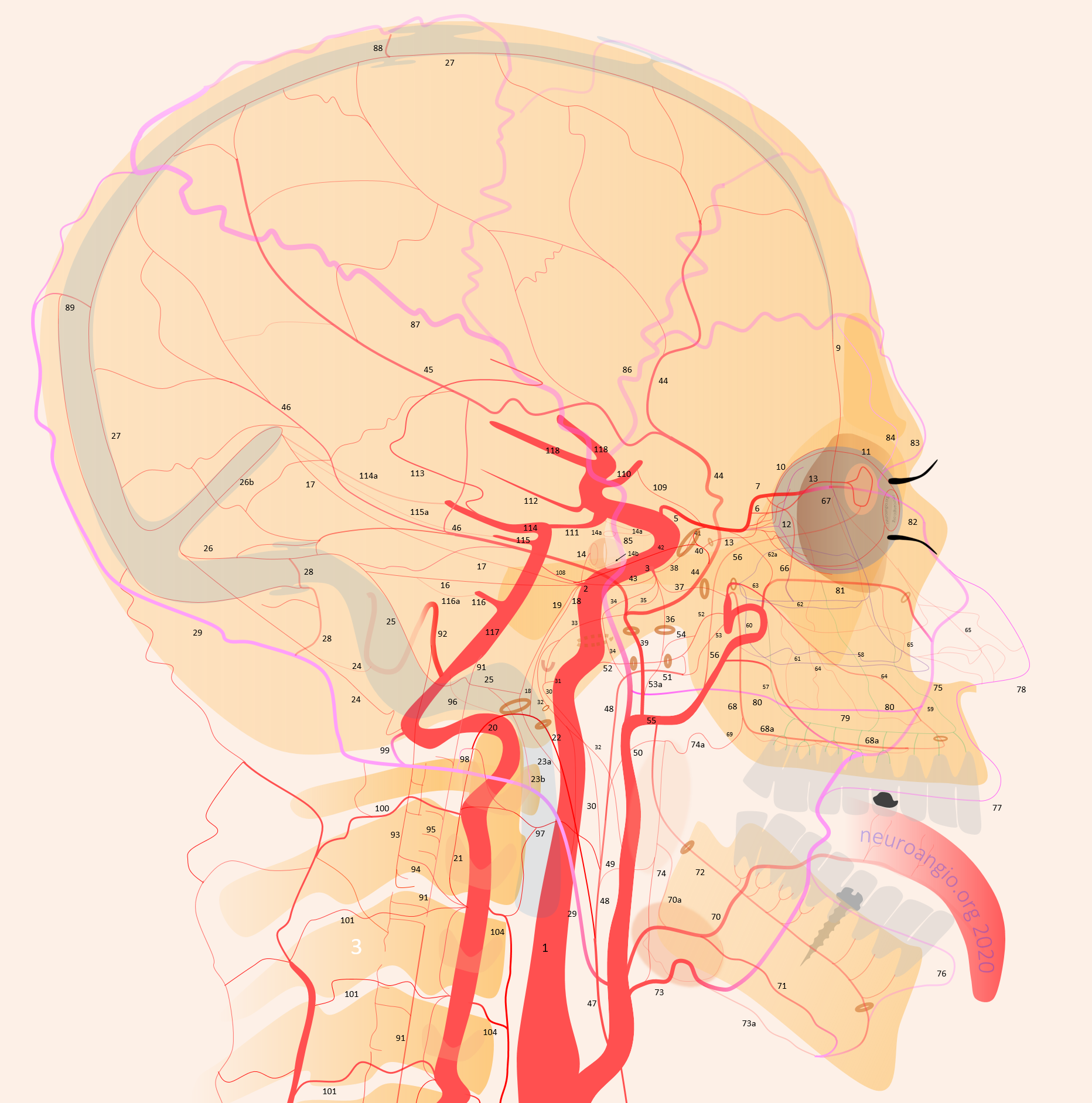
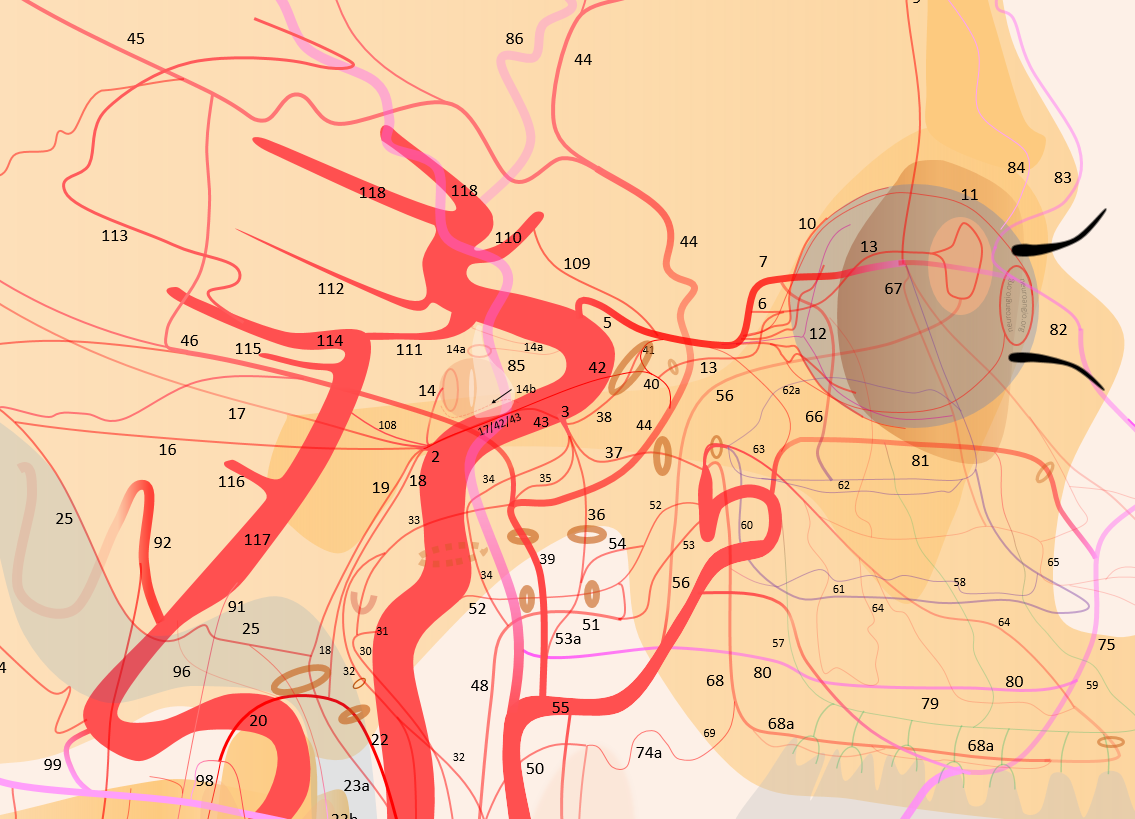
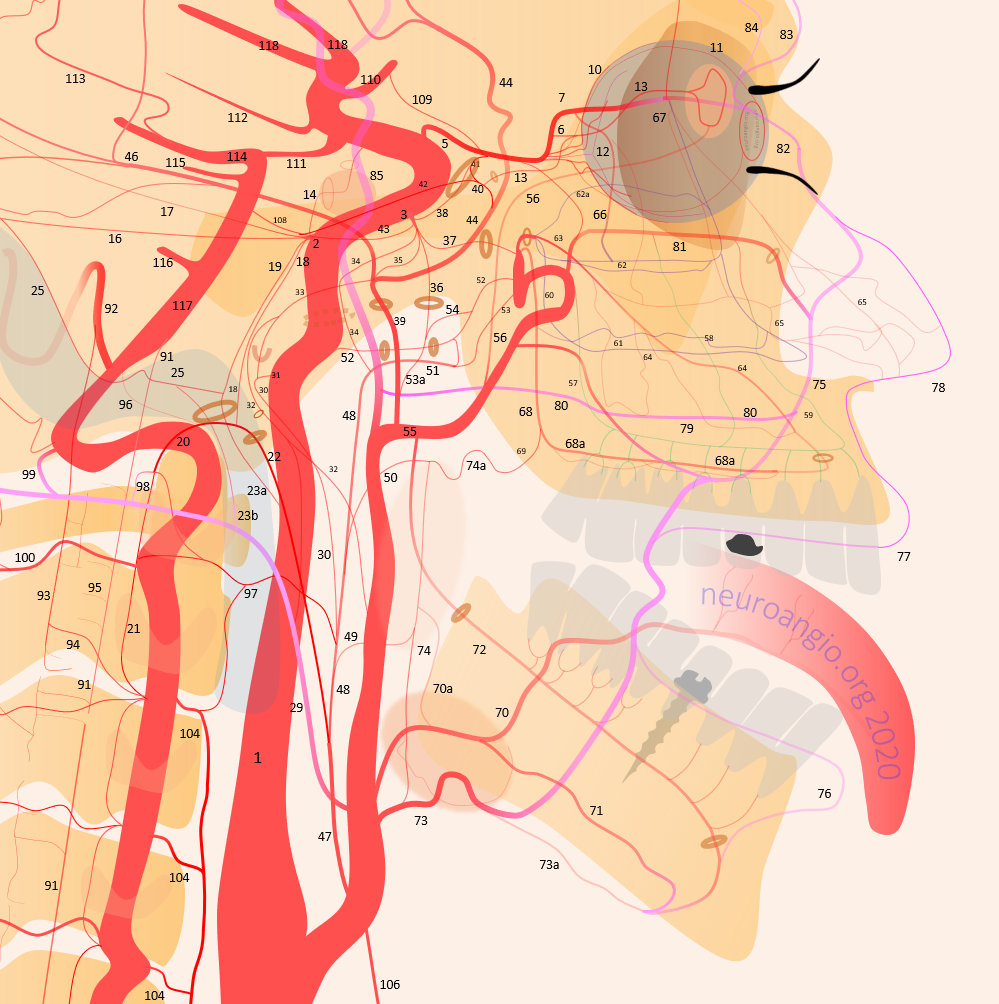
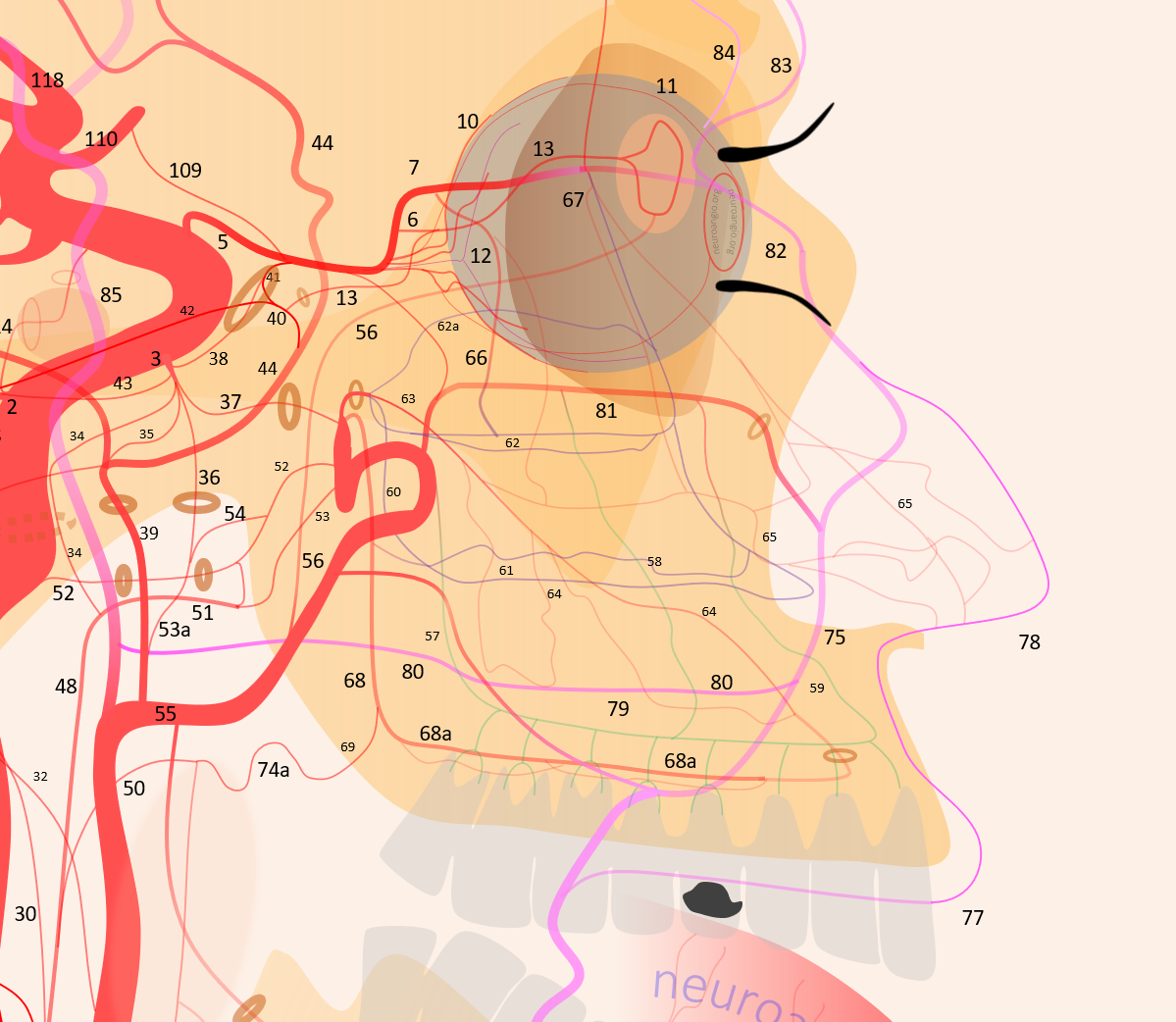
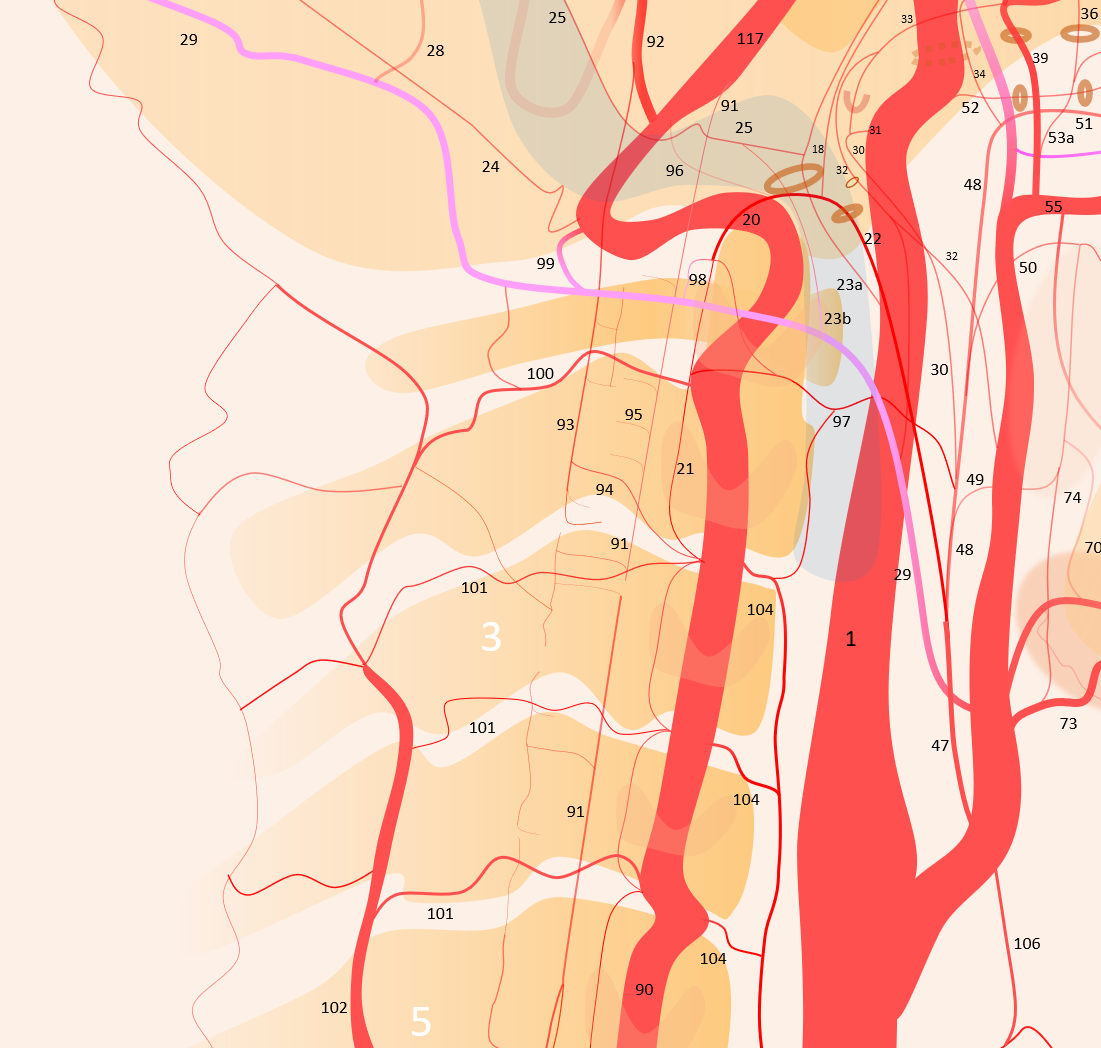
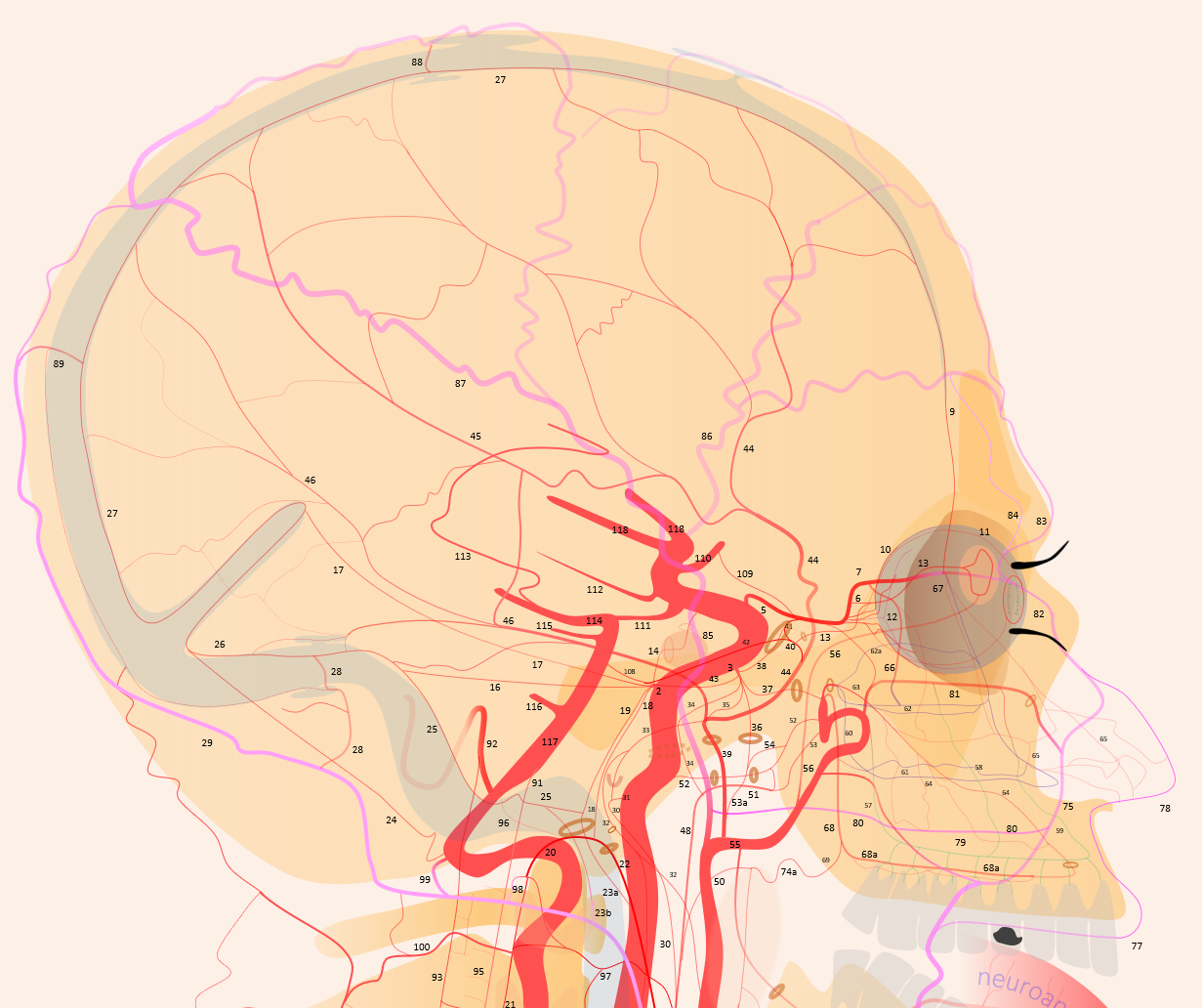
1 – internal carotid; 2 – MHT; 3 – ILT; 5 – ophthalmic artery, 6 – “loop” intraorbital segment, 7 – distal intraorbital segment; 8 – ethmoidal (anterior and posterior ) branches – same as 67; 9 – anterior meningeal / anterior falcine; 10 – short ciliary; 11 – long ciliary; 12 – central retinal; 13 – lacrimal; 14 – inferior hypophyseal; 14a – superior hypophyseal; 14b — McConnell Capsular; 15 – intercavernous (not shown) see skull base diagram; 16– lateral tentorial arcade; 17 – marginal tentorial / Bernasconi-Cassinari; 18 – medial clival arcade; 19 lateral clival arcade; 20 – hypoglossal branch to the odontoid arcade; 21 – odontoid arcade (ventral epidural arcade of the dens); 22 – hypoglossal division, AP artery; 23 a – jugular division, AP artery origin; 23b – jugular branch, occipital origin; 24 – posterior meningeal / tentorium cerebelli branch; 25 – sigmoid sinus arterial arcade (posterior meningeal system); 26 – transverse sinus arterial arcade (posterior meningeal system), 26a — straight sinus artery; 27 – SSS arterial arcade, 28 – transmastoid branch of OA (posterior meningeal system), 29 – OA; 30 – inferior tympanic branch, AP; 31 – caroticotympanic branch (remnant hyoid artery); 32 – stylomastoid branch (OA or posterior auricular artery, part of facial arcade); 33 – petrous branch, MMA, part of facial arcade; 34 – foramen Lacerum branch, AP; 35 – cavernous branch of MMA – same artery as spinosum branch of ILT; 36 – foramen Ovale branch of ILT– same vessel as intracranial branch of AMA; 37 – foramen rotundum branch (ILTor IMAX); 38 – anteromedial branch, ILT (remnant dorsal ophthalmic artery); 39 – MMA; 40 – sphenoid ridge branch; 41 – deep recurrent meningeal branch; 42 – clinoid tentorial arcade; 43 – posterior branch, ILT; 44 – frontal or anterior branch, MMA; 45 – parietal or posterior branch, MMA; 46 – petrosquamosal branch, MMA; 47 – Ascending Pharyngeal Artery (APA); 48 – pharyngeal trunk, APA; 49 – inferior division, APA; 50 – middle division, APA; 51 – superior division, APA; 52 – vidian artery; 53 – pterygovaginal artery; 53a — accessory meningeal artery; 54 – cutaneous branch (Eustachian branch), AMA; 55 – IMAX; 56 – anterior deep temporal branch; 57 – posterior 58 – middle 59 – anterior superior alveolar; 60 – sphenopalatine artery lateral nasal branch mainly supplying inferior (61), middle (62) and superior (62a) turbinates; 63 – mesial branch of the sphenopalatine artery, supplying posterior (64) and anterior (65) nasal septal systems, together with the corresponding posterior (66) and anterior (67) ethmoidal arteries; 68 – descending palatine; 68a — greater palatine; 69 – lesser palatine; 70 – lingual; 71 – submental; 72 – inferior alveolar; 73 – facial; 73a – submandibular; 74 – ascending palatine; 75 – angular; 76 – inferior labial; 77 – superior labial; 78 – superficial nasal; 79 – buccal; 80 — transverse facial; 81 – infraorbital; 82 – dorsal nasal; 83 – supratrochlear; 84 – supraorbital; 85 – Superficial Temporal Artery; 86 – frontal / anterior br. STA; 87 – parietal/posterior br. STA; 88 – STA / MMA anastomosis; 89 – OA / MMA anastomosis; 90 – Vertebral Artery; 91 – ASA; 92 – PICA; 93 – lateral / posterior spinal artery; 94 – coronary arteries; 95 – sulco-commissural arteries; 96 — hypoglossal nerve br; 97 – musculospinal br with C1 and C2 AA anastomoses; 98 – OA C1 nerve root branch; 99 – OA C1 muscular VA anastomosis; 100 – C2 muscular br.; 101 – segmental muscular branches; 102 – deep cervical artery; 103 – ascending cervical artery and its anastomoses (104) with VA; 105 – supreme intercostal; 105 – inferior thyroid; 106 – superior thyroid; 107 – supreme intercostal; 108 – trigeminal; 109 – ventral ophthalmic; 110 – anterior cerebral; 111 – posterior communicating; 112 – anterior choroidal; 113 – posterior choroidal; 114 – posterior cerebral; 115 – superior cerebellar; 116 – AICA; 116a — labyrinthine; 116b — subarcuate; 117 – basilar; 118 — middle cerebral
Its a work in progress. Any suggestions email neuroangio@neuroangio.org
